A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is the sweet spot between shared and dedicated hosting—offering power, flexibility, and security without the high cost. It provides you with your own virtual environment on a physical server, free from the constraints of having to share your resources with other customers.
As more than 35% of businesses now rely on VPS hosting for stability and performance, understanding how it works can help you make a smarter choice for your online presence. The lack of previous experience in server management is no longer an issue, as you can always find reliable managed services to take all technicalities off your hands.
Our task for today is to break down what a VPS really is, how it functions, who can benefit from its power, and why virtual servers have become the go-to solution for modern hosting needs.
What is a VPS?

Let’s start with the basics and explain what a web hosting server is. In basic terms, it’s a computer not too dissimilar to the one you have at home. It features a multi-core Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, and a data storage device. The main difference between a server and a regular computer is that a server is much more powerful.
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a virtualized environment that functions like a dedicated server, even though it exists within a larger physical machine. Through virtualization technology, a single powerful physical server can be divided into several smaller, independent virtual servers. Each of these virtual instances acts as its own server, complete with its own operating system, allocated CPU power, memory, storage, and bandwidth. This setup allows users to enjoy many of the benefits of having a dedicated server—such as control, flexibility, and security—without the higher costs associated with maintaining an entire physical machine.

How Does a VPS Work?
At the core of VPS hosting is virtualization technology, which is typically powered by a software layer called a hypervisor. The hypervisor’s role is to create and manage multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. It allocates a portion of the system’s hardware resources—such as CPU cores, RAM, and disk space—to each virtual server. Importantly, these virtual environments are fully isolated from one another.
Each VPS runs its own operating system (OS), which allows users to install software, configure services, and manage their environment independently—just as they would on a standalone physical server. This isolation and independence make VPS hosting particularly popular for developers, small businesses, and website owners who need more control and reliability than shared hosting can offer, but at a lower cost than renting an entire dedicated server.
Another key advantage of VPS technology is resource efficiency. Instead of leaving portions of a powerful server underutilized, virtualization ensures that computing resources are distributed dynamically among multiple users. This results in improved performance and reduced operational costs for both hosting providers and their clients.
What is VPS Hosting?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a hosting setup where a single physical machine is divided into several virtual environments, each functioning as an independent server. Every VPS instance runs its own operating system, has dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage, and can be configured separately from the others. The key idea is that virtualization software — typically a hypervisor — isolates these environments, so activities on one VPS do not affect the others.
However, traditional VPS hosting relies on a single physical server, which imposes inherent limits. If that server goes down or reaches its capacity, all hosted virtual machines are affected. In contrast, cloud VPS hosting distributes virtual servers across a network of interconnected machines, allowing resources to be scaled dynamically and downtime to be minimized through redundancy. This shift toward cloud-based VPS has made conventional, hardware-bound VPS hosting increasingly obsolete, as modern applications demand greater reliability, scalability, and resource elasticity than a single-node setup can provide
VPS Hosting vs. Shared Hosting
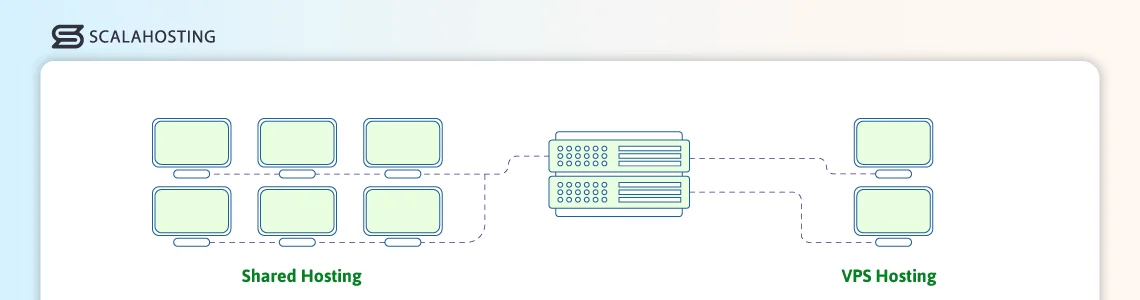
Comparing two of the most popular hosting services, VPS hosting and Shared hosting, we can see some distinct differences:
- Resource Allocation
In shared hosting, all users share the same server resources, like CPU and RAM. Should one user start taking up more—all other clients on the same physical machine will suffer. In a VPS, each user is isolated, guaranteeing dedicated resources and service stability . - Performance
Since shared hosting users compete for the same resources, heavy traffic on one site can slow others down. A VPS isolates each environment, so performance remains consistent regardless of other users. - Control and Customization
Shared hosting offers limited control — users can’t install custom software or modify server settings, as this would affect all other clients as well. VPS hosting provides root or administrative access, allowing full control over configurations and applications. - Security
Shared environments are more vulnerable since multiple users operate on the same system. If a hacker manages to gain server access from an unsecured account – all users are in danger. A VPS, on the other hand, offers stronger isolation, reducing the risk of cross-account security issues. - Scalability
Shared hosting has fixed resources and limited upgrade options. With a VPS, you can easily scale CPU, memory, and storage as your needs grow. - Cost
Shared hosting is cheaper and best suited for small websites with modest traffic. VPS hosting costs a bit more but delivers much better control, security, and performance. This is ideal for growing businesses or resource-intensive projects.
VPS Hosting vs. Dedicated Servers
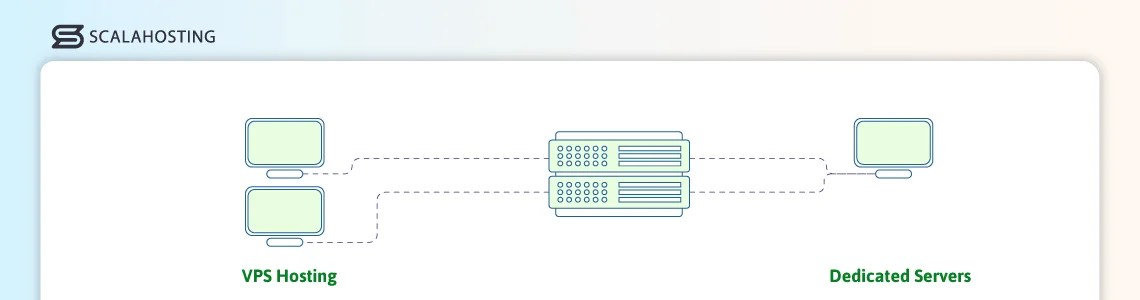
- Resource Allocation
VPS Hosting shares physical hardware with other virtual servers, but each VPS has allocated CPU, RAM, and storage. In comparison, all hardware resources are reserved for one user on a dedicated server—there is no sharing at all.
- Performance
Site loading speeds are generally consistent on a virtual server but can still be influenced by the host node’s overall load. Dedicated machines deliver a more predictable performance as you are the only user on the physical server.
- Control and Customization
You can enjoy full root access and flexibility on a VPS, with only possible limitations coming from the choice of virtualization software. The same is pretty much valid for dedicated services, though no virtualization layer exists.
- Security
Offers good isolation, but still shares the underlying hardware with other users. The dedicated machine, while isolated, is still prone to hardware issues. Such problems do not exist on a cloud VPS setup, as you have an entire network of interconnected servers, which offer true redundancy.
- Scalability
VPS hosting is definitely easier to scale as its resources can often be adjusted without any downtime. If you want to scale a dedicated server, however, you must either undergo physical upgrades or migrate to an entirely new machine with improved hardware.
- Cost
One of the biggest advantages of VPS hosting, the service is much more affordable due to its shared physical infrastructure and optimal resource usage. Dedicated servers are significantly more expensive, and the cost is only justified with very heavy workloads.
What is Managed VPS Hosting?
The thing about VPS hosting is that many users are afraid they don’t have the time or experience to manage their own virtual server. This is somehow justified. While providers do their best to ease clients with intuitive control panels and a rich knowledge base, not every business owner can afford to dedicate the time and effort needed to master this environment.
This is where managed VPS services come into play!
This type of plan combines the efficiency of a virtual server with the professional assistance of your hosting provider. The support team takes care of all technicalities—initial server setup, software installations, hardware replacement, issue resolution, etc. This allows the client to focus solely on their online project and business development.
Managed VPS hosting is highly preferred from startups and SMBs, eliminating the need for in-house server administrators.
What is Unmanaged VPS Hosting?
Naturally, not every hosting user is a novice with little to zero technical experience. More advanced users have different needs than complete beginners—they favor flexibility, customization control, and security configurations beyond the basics.
For them—unmanaged VPS hosting is a perfect solution.
Ideal for experienced developers and power users, self-managed services give you the bare-metal server, which you can operate as you wish, It’s like a blank sheet of paper that you can turn into a work of art.
On an unmanaged VPS plan, your hosting provider supplies the server and takes care of its initial configuration. From there on—you can use the root access to customize every little aspect of your online project. There is no technical support from the host and practically no limitations how you use the virtual server.
Why Should You Choose a VPS?
Choosing a virtual private server is often the logical next step for anyone who has outgrown shared hosting. A VPS bridges that gap by offering a balance between control, speed, and affordability.
Here are some of the main VPS hosting benefits:
- Dedicated Resources:
Your VPS gets its own share of CPU power, memory, and storage — ensuring that other users on the same host don’t slow you down. - Full Root Access:
You have administrative control over your environment, meaning you can install custom software, tweak configurations, and run specialized applications. - Better Stability and Reliability:
Because VPS instances are isolated from each other, one user’s spike in traffic or software issue won’t affect your server uptime or performance. - Scalability:
You can easily add more resources to your VPS plan as your project grows, without migrating to a new physical server. - Enhanced Security:
Each VPS operates in a sandboxed environment, minimizing the risk of cross-account vulnerabilities. - Cost Efficiency:
VPS hosting provides many of the capabilities of a dedicated server at a fraction of the price, making it a cost-effective middle ground.
When Should You Switch to VPS Hosting?
The right time to move from shared hosting to a VPS usually comes when your website or application starts to outgrow the limitations of a shared environment. Shared hosting is designed for small projects with low traffic and minimal technical demands — but as your audience, data, or performance needs expand, the cracks start to show.
Here are a few clear signs it’s time to upgrade:
- Frequent Slowdowns or Downtime:
If your site struggles to load quickly or becomes unavailable during traffic peaks, shared hosting may no longer be able to handle the load. A VPS gives you dedicated resources to maintain consistent performance. - Higher Traffic Volume:
Once your daily visitors or concurrent users increase beyond what your shared plan can handle, switching to a VPS ensures your website remains responsive and stable. - Need for Custom Software or Server Configurations:
Shared hosting limits what you can install or modify. VPS hosting provides root access, letting you tailor your server to your exact needs. - Security or Compliance Requirements:
Projects involving sensitive data, ecommerce transactions, or regulatory standards often need better isolation and control—something a VPS naturally provides. - Growing Business or Application Complexity:
As your website turns into a business platform or your application adds new features, VPS hosting offers the scalability to keep up without starting over.
In short, you should switch to a VPS when your project demands more control, reliability, and room to grow.
Selecting the Right Operating System For Your VPS
Selecting the right operating system (OS) for your VPS is a critical decision that impacts performance, security, and ease of management. The choice typically boils down to Linux or Windows, each offering unique advantages.
But how can you know which OS will work best for your setup?
Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian are known for their stability, security, and open-source flexibility, making them ideal for developers and hosting web applications. They are the most popular OS choices for a VPS, because most people run Linux-based software solutions like WordPress or Joomla.
Windows Servers, on the other hand, provide a familiar interface and seamless integration with Microsoft products, making it a strong option for .NET applications or businesses reliant on the Microsoft infrastructure. Still, they are not that widely popular because the solutions come with a licensing fee. Moreover, they operate in a closed environment, meaning there is no possibility for modifications and further expansions with custom add-ons.
When choosing your VPS operating system, consider your technical expertise, software requirements, and long-term scalability to ensure the OS aligns with your goals.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing Your VPS Provider

Selecting the right VPS provider is a crucial step in building your online presence. With so many hosting companies offering a wide range of services, it’s essential to understand which features truly matter. The right provider can enhance your website speed, security, and overall performance, while the wrong choice can lead to downtime, poor support, and wasted resources.
Here are some key factors to consider when evaluating VPS hosts:
1. Performance and Reliability
Your server has a direct impact on your website’s speed and user experience. Look for a provider that guarantees high uptime (at least 99.99%, backed by a strong SLA) and uses modern hardware such as SSD or NVMe storage, which significantly improves data access speeds. Additionally, ensure their data centers are located in regions close to your target audience to reduce latency. Consistent performance ensures your applications run smoothly and your business remains accessible at all times.
2. Scalability
A good VPS provider should allow you to easily scale your resources—such as CPU, RAM, and storage—as your business grows. Scalability ensures you don’t outgrow your hosting plan or experience performance bottlenecks during traffic spikes. Flexible resource allocation lets you adjust your plan without downtime or complex migrations, keeping your operations uninterrupted.
3. Security Options
Security is non-negotiable when it comes to VPS hosting. Choose a provider that offers robust security measures such as DDoS protection, firewalls, malware scanning, and regular data backups. Some providers also include advanced features like two-factor authentication and encrypted connections for administrative access. Additional extras to consider include SSL certificates, CDN solutions, spam filtering, and more. The best VPS providers prioritize both server-level and network-level protection to safeguard your data from cyber threats.
4. Technical Support and Customer Service
Even experienced users occasionally need assistance. A reliable VPS provider should offer 24/7 customer support via multiple channels—live chat, email, and phone. Responsive and knowledgeable technical support can make a huge difference when resolving configuration issues or unexpected outages. Before committing, it’s wise to test the provider’s support responsiveness and review customer feedback on their service quality.
5. Operating System and Software Options
Different projects require different environments, so flexibility in operating system (OS) choice is important. The best VPS providers allow you to choose between various Linux distributions (like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian) and Windows Server editions. They should also support one-click installations for popular software, control panels, and content management systems, simplifying the setup process.
6. Pricing and Value for Money
While cost should never be the only factor, it’s important to ensure you’re getting value for what you pay. Compare the features offered across providers, including bandwidth limits, storage type, and additional services like backups or managed support. Some low-cost providers may cut corners on performance or reliability, so balance affordability with quality and long-term stability.
7. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Unexpected failures can happen even with the best systems, making backups essential. Look for a VPS provider that includes automatic backups and easy restoration options. Some hosts offer snapshot capabilities, allowing you to restore your server to a previous state instantly. Reliable backup policies can save you from data loss and minimize downtime during critical incidents.
8. User-Friendly Management Tools
Managing a VPS can be complex, especially for beginners. Choose a provider that offers an intuitive control panel or management dashboard. Custom dashboards like SPanel can significantly simplify daily tasks like monitoring resource usage, restarting the server, and deploying applications. The easier the management interface, the more control and flexibility you’ll have over your VPS environment.
Understanding and Enhancing VPS Security
Security is one of the most important aspects of managing a virtual server. While a VPS provides greater control and flexibility compared to shared hosting, it also places more responsibility on you to protect your environment. Without proper safeguards, your server can become vulnerable to data breaches, malware, or unauthorized access. Implementing strong security measures ensures the safety of your data, applications, and users.
1. Keep the System Updated
Regular updates are the first line of defense against cyber threats. Both the operating system and any installed software should be kept up to date to patch known vulnerabilities. Many attacks exploit outdated versions of software, so enabling automatic updates or setting up a maintenance schedule can prevent potential exploits before they occur.
2. Use Strong Authentication
Weak passwords remain one of the most common causes of server breaches. Always use complex, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible. For Linux servers, consider disabling direct root logins and using SSH key authentication instead.
3. Configure Firewalls and Network Protection
A properly configured firewall acts as a barrier between your server and unwanted traffic. Tools like iptables, UFW, or cloud-based firewalls help restrict access to only essential ports and services. Additionally, using services that provide DDoS protection (like a CDN) can shield your VPS from large-scale attacks aimed at overwhelming your resources.
4. Back Up Your Data. Always
Even the most secure systems can face unexpected failures. Regular automated backups ensure that your data can be quickly restored in case of an attack or accidental data loss. Backups should be stored in a secure, offsite location and tested periodically to confirm they can be restored without issues.
5. Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Continuous monitoring helps you identify unusual activity early. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) such as Fail2Ban or OSSEC can automatically block suspicious login attempts and alert you to potential breaches. Log monitoring tools also provide insight into server activity, allowing you to spot anomalies before they become serious threats.
6. Securing Data and Communication
All data transmitted to and from your VPS should be encrypted. Using SSL/TLS certificates protects sensitive information and builds trust with your users. Likewise, encrypting stored data adds another layer of defense in case someone gains unauthorized access to your system.
Selecting the Right Control Panel for Your VPS Server
A reliable control panel is essential for managing your VPS efficiently. It serves as the command center where you handle websites, emails, databases, domain names, security, and server performance without needing advanced technical skills. A good control panel saves time, reduces errors, and simplifies complex administrative tasks through an intuitive interface.
Popular options like cPanel, Plesk, and DirectAdmin offer strong functionality but often come with added licensing costs and/or limited flexibility.
That’s where ScalaHosting’s SPanel stands out.
Designed specifically for virtual server users, SPanel is a lightweight, multifunctional control panel that serves as a great alternative to cPanel, offering a license-free solution that helps reduce costs while maintaining full control and security. It includes built-in tools for website management, automatic backups, and resource analytics. SPanel also contains some unique innovations like SShield Security (malware monitoring) and WordPress Manager (WP management and security).
The great thing about Scala’s panel is the active user contribution. Every SPanel client can suggest new features and the ones that get the most upvotes are soon added to the platform.
Choosing the right control panel ensures a smoother VPS experience, balancing power, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. For many users, SPanel delivers the ideal mix of performance, usability, and value.
Managing Your VPS
Once your Virtual Private Server (VPS) is set up, effective management becomes key to maintaining stability, performance, and security. Proper VPS management ensures your applications run smoothly, resources are used efficiently, and potential issues are addressed before they impact your operations.
The first step in VPS management is monitoring performance. Keeping an eye on CPU, RAM, and storage usage helps prevent overloads and downtime. Most providers offer built-in monitoring tools, or you can use third-party solutions to track performance and receive alerts about unusual activity. Regular updates to your software core and add-ons are also essential, as they patch vulnerabilities and improve overall system reliability.
Security management is another crucial aspect. Implementing firewalls, maintaining strong authentication methods, and performing routine backups all help safeguard your data. Automated backup solutions and snapshot features can save time and ensure quick recovery if something goes wrong.
Finally, routine maintenance—such as clearing unused files, optimizing databases, and auditing user access—keeps your VPS running efficiently.
Using an intuitive control panel like SPanel can simplify these tasks by providing centralized management for your websites, emails, and security tools. With consistent attention and the right tools, managing your VPS becomes a straightforward process that ensures long-term reliability and peace of mind.
FAQ
Q: How do I choose a good VPS?
A: First, you need to make sure that the technologies powering your website are all supported. Check out the parameters of the virtual machine and see if it offers the most suitable operating system afor your software.
Once that’s taken care of, you can move on to the hardware resources. Getting the correct configuration may not be the easiest thing in the world, but if you talk to your host’s sales specialists, they may just be able to point you in the right direction. The good thing is, even if you get a VPS that is not powerful enough, upgrading it is pretty straightforward.
Q: Can I create my own VPS?
A: Many hosting providers let you choose the exact parameters of the VPS. You get to decide how many CPU cores, gigabytes of RAM, and disk space it’ll have, and the configuration can be completely customized.
Q: How do I access my VPS?
A: After the virtual server is deployed, your VPS provider will send you instructions on what you need to do to access it. If you’re running Linux, you will most likely be able to log into the server via SSH. Often, the VPS comes with a web hosting control panel that automates and simplifies many server management tasks.
What is a VPS – Everything you need to know!


