What Is Cloud Hosting?
Imagine your online store crashing right in the middle of a big sale – frustrated customers, lost revenue, and mounting stress. Many small business owners have faced this challenge, and it’s often due to the limitations of traditional web hosting.
That’s where cloud hosting steps in.
Instead of relying on a single physical server, cloud hosting runs your website or app on virtual servers that draw power from a network of interconnected physical servers. This setup means your site can scale easily, stay reliable under heavy traffic, and save you money in the process.
In this guide, we’ll break down what cloud hosting is, how it works, and why it’s a game-changer for businesses in 2025. As companies continue shifting online – with Gartner predicting that 85% of enterprises will use cloud hosting by 2025 – understanding this technology is key to staying competitive in a digital-first world.
What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is like having your website live in a vast, flexible network of servers “in the cloud,” allowing it to access resources whenever it needs them. Instead of relying on a single physical computer in a data center, your website draws power from multiple connected servers worldwide.
There are several components that are key to this technology:
- Virtual servers (VMs) – using a process called virtualization, a provider can split a single physical server into multiple virtual servers, each with its own dedicated resources. When we have more than 3 different interconnected servers doing that, we can talk about true cloud hosting
- Cloud infrastructure – Behind the scenes, cloud hosting providers manage an entire ecosystem of servers, storage systems, and network connections. This infrastructure is designed for resource scalability and uninterrupted uptime. If any single server in the ecosystem fails, another instantly takes over, keeping your website running smoothly.
- Pay-As-You-Go model – With cloud hosting, you only pay for what you use. It’s similar to your electricity bill – you’re charged based on how much power you consume, not a fixed monthly fee for a specific amount of hardware.
Think of traditional hosting as buying DVDs: you own the hardware (the DVDs and DVD player), and you’re limited to what you’ve purchased. Cloud hosting, on the other hand, is like streaming movies on Netflix – you don’t need to own any physical discs; instead, you can instantly access whatever you want, whenever you want, as long as you have an internet connection.
What is a Cloud VPS?
A Cloud VPS builds upon the concept of a traditional Virtual Private Server but takes it to the next level – a VPS on steroids, if you will.
While a traditional VPS runs on a single physical server, a Cloud VPS operates within a network of interconnected machines – a cloud cluster. In this setup, your virtual server draws its computing power, storage, and other resources from a distributed pool of servers working together.
In a traditional VPS setup, all virtual instances are created and hosted on one physical server. This design works in general, but it has its limitations. If the physical server fails or runs out of resources, every VPS on it is affected. Worse still, fixing the issue often requires manual intervention, downtime, and in extreme cases, migration of the entire virtual machine to a different server.
By contrast, a Cloud VPS eliminates most of these restrictions by spreading virtual instances across multiple servers in a cluster. Resources are dynamically allocated, so if one physical node fails, the system automatically shifts workloads to another without interruption.
Another key distinction is scalability. With a traditional VPS, you’re limited to the resources of the host machine. A Cloud VPS, on the other hand, enables nearly instant scaling without requiring a reboot or manual data movement. The cloud cluster provides an enormous, expandable pool of hardware resources, making the hosting service that much more flexible.
All this means that the service is very cost-effective. You only pay for the resources you actually use, which is great for businesses on a budget. This contrasts the much more expensive dedicated hosting where you get an entire physical server and pay for its resources regardless if you use them or not.
What is Cloud VPS Hosting?
Cloud VPS hosting blends the control of a private server with the flexibility of cloud computing – which explains why it’s one of the most in-demand services of this type.
In cloud VPS hosting, the provider maintains a large pool of physical machines linked together to form a cloud cluster. Virtual servers are deployed within this cluster using virtualization technology, and their resources – CPU, RAM, and storage – are drawn dynamically from the pool rather than tied to a single piece of hardware. This interconnected design means that if one physical server experiences a problem, the rest of the machines in the cluster immediately step in to handle the workload. As a result, cloud VPS hosting delivers exceptional uptime and high fault tolerance.
Another defining advantage of cloud VPS hosting is its instant scalability. In a traditional VPS setup, changes to the hardware configuration usually require manual upgrades or site migrations. By contrast, a cloud VPS allows you to scale resources on demand, with no service interruptions or downtime.
For instance, imagine you run an ecommerce website in the middle of a Black Friday sale. Traffic surges and your virtual server is nearing its RAM limit. With a traditional VPS, you might need to open a support ticket and wait for someone to add more memory manually. In a cloud VPS environment, you can adjust your resource allocation with a click and instantly handle the extra traffic.
How Does Cloud Hosting Work?

Three key technologies are involved in every cloud hosting setup. Virtualization is used for the abstraction and distribution of hardware resources, data replication ensures all servers in the cluster can work for the hosted projects, and load balancing is there to guarantee that the hardware stays healthy.
- Virtualization enables multiple operating systems and applications to run concurrently on a single shared physical hardware. This means that hosts can divide any server into multiple instances that operate independently from each other. Popular virtualization technologies include OpenVZ, KVM, and VMWare
- Data replication ensures your server’s constant availability. Your files, databases, and configurations are mirrored (copied) across multiple servers. If one server fails, another immediately takes over – often without any noticeable downtime.
- As users continue to visit your site, the system automatically distributes incoming requests across multiple servers using load balancing. Its job is to prevent any single machine from becoming overloaded. If one server is under heavy load, traffic is rerouted to another healthy server within the network.
Now, let’s look at a flowchart of what a typical user request looks like:
[Visitor’s Browser]
↓
[DNS Lookup: Finds Cloud Network]
↓
[Load Balancer]
↓
[Virtual Servers Pool]
├── VM1 (CPU/RAM/Storage)
├── VM2 (Backup/Load Share)
└── VM3 (Auto-scaled Instance)
↓
[Data Redundancy: Files Mirrored]
↓
[Webpage Delivered to User]
To summarize, cloud hosting works by pooling computing resources across a network of interconnected servers. It utilizes virtualization, load balancing, data redundancy, and auto-scaling to provide unmatched performance, uptime, and security.
Traditional vs. Cloud Hosting
| Feature | Traditional Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Runs on a single physical server. | Uses a network of multiple interconnected servers. |
| Resource Allocation | Fixed CPU, RAM, and storage – limited to one machine’s capacity. | Resources are pooled and allocated dynamically from several servers. |
| Scalability | Scaling requires manual upgrades or migration. | Instantly scalable – resources adjust automatically to traffic demand. |
| Performance | Performance can drop if the physical server is overloaded. | Load balancing distributes traffic for consistent performance. |
| Reliability | Single point of failure – if the server crashes, downtime occurs. | High redundancy – data mirrored across multiple servers ensures uptime. |
| Cost Model | Pay for a fixed plan (whether fully used or not). | Fixed or Pay-as-you-go – only pay for the resources you actually use. |
| Best For | Websites with steady, predictable traffic. | Growing businesses or sites with variable or high traffic. |
Think of traditional hosting like renting one physical office – limited space and fixed capacity.
Cloud hosting is like having access to an entire office complex – you can expand or shrink space as your needs change, instantly and efficiently.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting
In a cloud hosting environment, your website doesn’t rely on a single physical machine. Instead, the host builds a cluster of interconnected servers called a cloud, which provides a vast pool of resources to be distributed among individual accounts.
The evolution of cloud technologies has been the single most significant leap in the evolution of the web hosting industry. It presents providers with a completely new approach to distributing hardware resources, and it gives website owners a number of advantages. Namely:
- Performance: The hosting service is built on top of a robust distributed infrastructure that uses enterprise-grade hardware and a fast internet connection to boost your site’s loading speeds.
- Scalability: When the entire hosting service depends on a single server, scalability is limited to the physical machine’s capabilities. In the cloud, you can tap into an enormous resource pool and enjoy pretty much infinite room for growth.
- Flexibility: The cloud cluster allows you to specify exactly how much processing power, memory, and storage you need without sticking to preset plans. In addition, virtualization enables hosts to build a fully customizable hosting environment, letting you run all the software and services you need.
- Reliability: If one of the cloud servers goes down, the other nodes are on hand to pick up the slack and keep downtime to a minimum.
- Cost efficiency: Cloud technology lets hosting providers tailor your account’s configuration to your exact requirements. On the one hand, this allows them to utilize their hardware more efficiently, which makes the service more affordable. On the other, you can have the performance you’re after without paying for resources you don’t use. According to a Forrester research, cloud hosting can reduce your costs with up to 40%.
- Security – Working with a network of servers eliminates the possibility of a single point of breach. On top of that, the risks of hacking attempts like DDoS attacks are minimal, because your project is distributed between multiple servers on different locations.
- Redundancy: In a cloud environment, your information is usually replicated across multiple devices, minimizing the risk of data loss.
- Global reach – it doesn’t matter if your target audience is in Europe, Asia, or North America. The cloud technology means you always have a server close to your users, wherever they are.
In other words, there are more than a few reasons for choosing a cloud-based service.
Types of Cloud Hosting
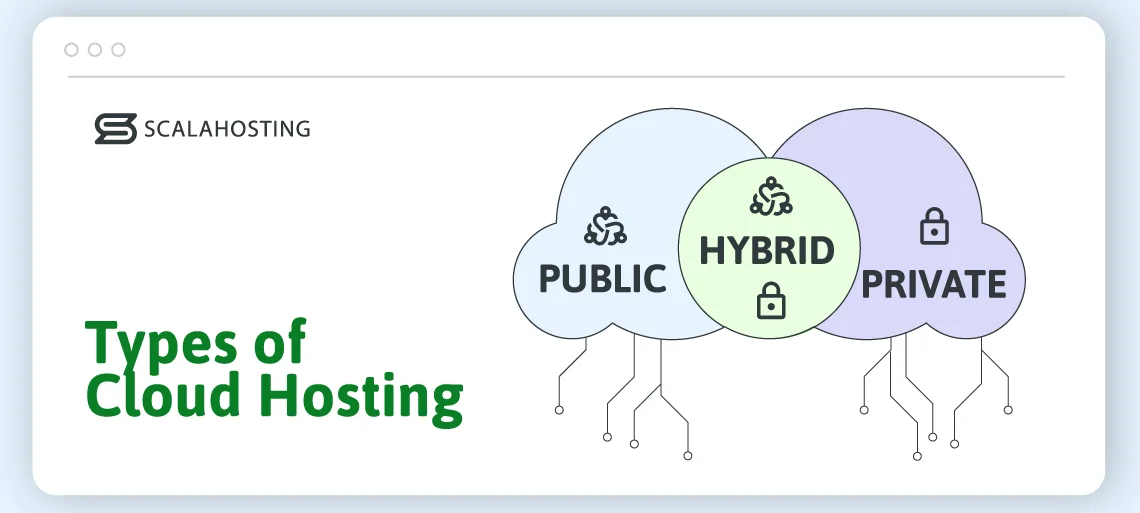
Cloud hosting’s remarkable versatility is mainly due to the multiple approaches to building a cloud cluster. Depending on your technology and security requirements, you can create three main types of setups:
Public cloud
The services relying on public cloud infrastructure are perfect for anyone looking to overcome the limitations of traditional web hosting. Whether your personal blog is taking off or you’re planning on launching an ecommerce project and want consistent performance and enhanced security, public cloud hosting is the perfect environment for you.
It also works for mobile applications, software development and testing, and collaboration platforms.
- Hardware
The physical servers are owned, managed, and maintained by the provider. The hardware is deployed in data centers run by the hosting company, and sometimes, machines belonging to the same cloud can be situated in multiple locations across the globe, providing low-latency services to customers around the world.
- Virtualization
Virtualizing the hardware resources provided by the cloud’s nodes is crucial for efficiently utilizing and distributing them among customers. Depending on the service on offer, hosts use either hypervisors to create virtual machines or containerization technology to define separate hosting environments for individual projects.
- Isolation
Multiple website owners use the same cloud cluster. However, thanks to the implemented virtualization techniques, all projects are fully isolated. You don’t need to worry about another account experiencing a traffic spike and compromising your performance.
- Management
Depending on the setup, the host may have a system that automatically scales individual accounts. If it doesn’t, the user must request upgrades and downgrades. In both cases, scalability in the cloud is seamless.
Private cloud
A private cloud is run and managed by the organization that uses it. Building and maintaining it isn’t cheap, so the setup is usually used by large corporations and government institutions. Most private cloud infrastructures don’t make the data they host widely available, so they’re perfect for the financial and healthcare sectors, where information must be stored securely.
- Hardware
The organization building the private cloud usually owns the servers in it. The machines can be deployed on premises or in a data center, but they’re always managed by the owner’s sysadmin team.
- Virtualization
A virtualization layer connects the servers in the cluster and shares data between them. Sysadmins may need to isolate individual projects in separate environments, and the technology they’ll use depends on their specific requirements.
- Networking
Members of the organization owning the private cloud must be able to connect to it and access its resources securely. This is usually achieved through a VPN.
- Security and monitoring
A private cloud usually hosts a lot of sensitive information, so its owner must ensure the proper measures have been taken to eliminate the risk of unauthorized access. These include anything from a properly configured firewall to data encryption and strict identity and access management policies.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud setups combine the benefits offered by public and private cloud solutions. With them, companies have complete control over a large part of the infrastructure but can still take advantage of the scalability associated with a public cloud setup.
Hybrid cloud solutions aren’t particularly widespread, but they can be useful in a few scenarios. For example, when vast volumes of sensitive data must be processed, the owner may use their private servers for storage while employing the power provided by a public cloud setup for analysis.
Some ecommerce platforms may also use private cloud servers to store sensitive payment data while deploying the customer-facing part of the app in a public cloud environment.
- Hardware deployment
A hybrid setup mixes public cloud services offered by a commercial provider with privately configured infrastructure. The private hardware can be deployed either on-site or in a data center. Some organizations also use edge devices to handle latency-sensitive tasks.
- Integration
Hybrid cloud setups rely on tools that bridge the gap between the public and private sections of the infrastructure. These utilities are heavily specialized and facilitate the secure communication between individual nodes.
- Data layer
Another vital component of the hybrid cloud infrastructure ensures data is correctly replicated and synchronized between the public and private nodes. Yet again, this is achieved through specialized utilities that must be configured to the highest possible security standards.
- Connectivity
The hybrid cloud owner must ensure authorized personnel have access to all sections of the infrastructure. Access policies tend to be more complex in a hybrid cloud environment, and the utilities enforcing them are more sophisticated.
Managed Cloud and Unmanaged Cloud
This type of cloud hosting does not depend on the chosen infrastructure setup, but on the level of support you want to get with the service.
When you are on a Managed Cloud plan, you can rely on the full technical assistance of your hosting provider. This means the host’s experts can take care of your initial server setup, OS and software installations, firewall configurations, and issue resolution. The service is ideal for businesses that want to focus on business development without getting bogged down in technical details.
On the other end of the spectrum is the Unmanaged Cloud. This type of hosting targets developers and power users who want full customization freedom. The client gets a bare-metal server with initial OS setup. From there on – they can operate the environment as they wish. The user is responsible for all technicalities and has to resolve any obstacles that may arise.
How Do I Host a Website In the Cloud?

Dozens of cloud setups can cater to a typical website. For example, if you want to build a run-of-the-mill WordPress site, even a humble Docker container can do the job. However, setting it up is hardly novice-friendly.
First, you create the project directory and put together a special configuration file specifying the image you will be using. Docker then downloads and deploys the image, but it’s often up to you to install your website-building application before you can start work on the project.
At the very least, this requires some command-line work, which isn’t for everybody.
A more suitable option for many would be to use a cloud-based VPS. VPS stands for virtual private server, and when it’s deployed in the cloud, it’s one of the best web hosting solutions out there.
For the most part, it has all the characteristics of a regular physical machine. However, the cloud infrastructure powering it brings a few benefits that can be critical for your site’s development:
- Guaranteed resources
Every VPS plan comes with its own set of hardware resources. You choose how many CPU cores, how much memory, and how much storage space you’ll use.
These resources are reserved for your project only and are available 24/7. This makes the performance not only stronger but also more consistent and predictable.
- An isolated environment
Your project’s performance and security aren’t affected by other people’s actions. Your VPS may be deployed on the same hardware cluster as other virtual servers, but it’s a fully isolated service.
- A customizable hardware configuration
Server management platforms like SPanel often allow you to monitor how your website utilizes the available resources, which, combined with the freedom provided by the cloud setup, enables you to create a configuration that gives you impeccable performance while keeping the service cost-efficient.
For example, if you need more processing power, but your server’s memory and storage are sufficient, you can add a CPU core without adjusting the RAM or SSD space.
- A customizable software environment
Because a VPS is a standalone machine. It has its own operating system, and the environment it provides can be tailored to your specific needs. With a managed server, this will be the responsibility of your hosting provider. If you have a self-managed plan, you have to do it yourself. However, in both cases, you can build the setup exactly how you want it.
Who Should Use Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting shines in environments where scalability, reliability, and flexibility directly impact your business’s chances of success. Over the years, we’ve seen it play a key role in the growth of numerous projects, and it’s been particularly beneficial in industries where uptime and a reliable hosting infrastructure are of utmost importance. Here are a few examples:
- Ecommerce
Two of cloud hosting’s main advantages make it particularly useful for online stores. First, it helps ecommerce business owners achieve excellent loading speeds and a perfect user experience. This is the most surefire way of converting an accidental visitor into a paying customer. Secondly, but just as importantly, is the flexibility. Cloud hosting solutions are notoriously easily scalable, and this is definitely something you need if you want to run a successful online store.
For one, the scalability allows you to adjust your platform’s capabilities quickly and easily, which means you can maintain excellent performance as your business grows. You can also be extra flexible when you need to. For example, traffic typically increases around Black Friday and the holiday season, which should be no problem for you, as you can adjust your account’s hardware configuration and meet the increased demand. Then, when things go back to normal, you can revert to the previous configuration and keep your hosting bills at bay for the rest of the year.
- Media and publishing
Traffic fluctuations on a news website can be caused by a number of events. It could be a meeting of world leaders discussing the planet’s future or a pop star spotted wearing an engagement ring – an influx of new visitors is always just around the corner.
A properly configured cloud hosting service gives you the best chance of meeting the increased load without a drop in performance. However, the setup’s advantages shine not just during traffic spikes.
News reporting is a notoriously competitive sport. Every hit is important, and the heat is on to convert as many accidental visitors as possible into regular ones. Although it’s hardly the only factor, website performance can contribute to a website’s credibility and make people choose one outlet over another as their primary source of information.
- Corporate and business websites
When you want to find information about a particular business, be it a large corporation or a hairdresser located up your street, you go online and try to find its website. If the site is down or takes ages to load, you’ll likely lose interest quickly. For the business, this means lost revenue and credibility damage that could be tricky to repair.
There’s more to it than that, though. Even relatively small companies use a wide range of applications to manage customers and inventory and delegate tasks among team members. These solutions are often integrated with their customer-facing websites, meaning they need a hosting platform that provides reliable performance and as few service disruptions as possible. A cloud hosting infrastructure’s built-in redundancy and load balancing mechanisms ensure just that.
- Membership and community websites
The great thing about the internet is that it helps like-minded people connect and interact with ease. All you need to create an online community is a topic people can unite around and a website acting as a communication platform.
However, as the community grows, your hosting requirements will change. Only a cloud hosting solution can be flexible enough to meet them.
- Non-profit organizations
Cloud hosting is the most cost-effective service of this kind, and as such, is well-suited for startups and non-profit organizations that work on a tight budget. You only pay for the resources you use, so you can be sure you won’t be overcharged for things you don’t really utilize.
For the affordable price, non-profits can operate a powerful server that allows them to establish and grow their online presence without fear of being limited, suffering from poor performance, or losing their project due to insufficient security.
How to Choose a Cloud Hosting Provider

Not all cloud hosting providers are created equal, and if you don’t pick the right one, you won’t be able to take full advantage of the setup. So, what do you need to look out for when choosing a host?
- Ask about the infrastructure
Often, the difference between a traditional hosting plan and a cloud-based service isn’t immediately visible to the user. At the same time, “cloud’ has turned into a high-conversion marketing term that can be misused sometimes.
Before you choose a provider, contact its technical team and ask them about the infrastructure the service is built on. If you have any doubts that they may be selling you a traditional hosting service as a cloud-based one, it’s best to walk away.
- Ensure you have enough options to scale
Although cloud hosting solutions are inherently scalable, you must still ensure your project has enough room for growth. Ask the host’s support agents to show you how powerful your account can be and give you examples of the solutions they offer to customers with high demands.
On the one hand, these solutions must provide you with the performance you’re after once the project gains momentum. On the other, they should be flexible enough to ensure you develop your site without spending too much.
- Review the technology
Multiple virtualization techniques can be used to build a hosting environment on top of a cloud cluster, each with advantages, disadvantages, and limitations.
For example, KVM and OpenVZ are two of the most popular virtualization technologies. OpenVZ allows hosts to build virtual machines with very little overhead on the hardware resources, so it can help keep costs down. However, hosting solutions powered by KVM are more easily customizable in general, with support for numerous operating systems and software platforms. Review your project’s requirements and see which option fits them the best.
It’s not just about virtualization, though. Ultimately, your website is powered by the cloud’s hardware, and you must ensure it’s up to date. For example, modern SSD storage devices are several orders of magnitude faster than traditional HDDs. Signing up for an account that uses the old technology makes no sense nowadays.
- Find the best server location
Hosts have servers deployed all around the world. Often, when choosing a hosting account, you’re allowed to pick between multiple data centers. Make sure the provider you select has one located physically close to your target audience. The lower latency will result in faster loading speeds and a better chance of your site attracting regular visitors.
- Check the feature list
The tools you need to efficiently build your site depend on the project’s requirements and on your personal technical skills. For example, if your website requires a custom hosting environment, you’ll likely need a self-managed solution with root access and enough expertise to ensure you can change the correct server settings.
On the other hand, if your site’s setup is standard and your technical skills are a bit more limited, you’re better off with a managed hosting account. It comes with a control panel and a graphical user interface that automates and simplifies most of the tasks you need to go through.
- Ensure you can get quality technical support
Building and maintaining a cloud infrastructure is no mean feat. It requires a team of experts who know what they’re doing and can act quickly if something goes wrong. The same experts must also be on hand to assist you if you need help.
24/7 support is non-negotiable – website or security issues can’t wait for business hours. That’s not all, though.
There’s no point in having someone online if they take ages to respond, so before you commit to a purchase, open a support ticket or a live chat and see how quickly agents reply. Online reviews can also give you a clear idea of the speed and quality of the technical support offered by different providers.
- Make a direct provider comparison
It’s always a good idea to shortlist a few hosting companies and see how they stack up against each other.
What features are included in the package? At what price? Do they offer some kind of money-back guarantee? What is their migration policy? What about their backup and restore opportunities? What can you expect once your project starts to grow? Those are all questions you need to consider before making a final decision.
Future of Cloud Hosting
The cloud hosting industry is entering a transformative decade defined by speed, intelligence, and sustainability. As organizations continue to migrate workloads and modernize their infrastructure, new technologies are reshaping how cloud services are built and consumed.
What can we expect from the industry in the near future, tho?
One major trend is edge computing, which brings processing power closer to where data is generated. This reduces latency, helps speed up data traffic, and lays the foundation for real-time applications-such as autonomous vehicles, health monitoring, and even smart cities. Meanwhile, serverless architecture is changing how developers build and deploy software. By abstracting away infrastructure management, teams can focus purely on code and innovation, scaling automatically as demand fluctuates.
AI integration is another defining force that is already rocking the IT world. Cloud providers are embedding machine learning capabilities directly into their platforms, allowing businesses and individuals to make use of advanced analytics and automation with minimal setup. This democratization of AI means users can expect smarter tools, predictive insights, and faster decision-making capabilities to be integrated into everyday tasks.
Sustainability is also becoming a core priority. The rise of the green cloud reflects a growing effort to minimize energy use, rely on renewable power sources, and design data centers with carbon neutrality in mind.
According to IDC, by 2030, global cloud spending will hit $1 trillion, signaling not just growth, but a deeper reliance on cloud ecosystems. For users, this future promises easier access to AI-driven tools, smoother digital experiences, and consistently better performance regardless of their physical location.
Conclusion
Cloud hosting has become the smarter, more resilient choice for modern websites because it delivers scalability, reliability, and flexibility that traditional hosting can’t match. Whether you’re running an online store, a media outlet, or a growing community, the cloud ensures your site can handle today’s demands and tomorrow’s growth.
Now that you know what cloud hosting is, you’re equipped to make an informed decision for the best provider to match your needs.

FAQ
Q: What is managed cloud hosting?
A: Managed cloud hosting is a type of service where users can rely on their provider’s support team for assistance. Depending on the host, the scope of that assistance can vary, but it typically includes tasks such as server and OS setup, software installations, hardware replacement, security configurations, and issue resolution. The service is suited for startups, SMBs, and growing enterprises that want to focus on business development without dealing with technicalities.
Q: What types of cloud infrastructure are there?
A: Depending on the architecture and the purposes of the infrastructure, clouds can be categorized as public, private, or hybrid. Public clouds usually host websites and applications, and are generally used for making information accessible anywhere in the world. Private clouds usually support the IT infrastructure of large corporations and organizations. Hybrid clouds are employed when customer-facing assets must work in unison with backend systems.
Q: What is the best cloud hosting option for beginners?
A: Managed cloud VPS hosting is your best bet if your technical experience is limited. You get a virtual machine with guaranteed resources and a fully isolated hosting environment, so you can enjoy top performance and excellent security. At the same time, you manage your hosting account through a novice-friendly control panel with an intuitive graphical user interface.
Q: How much does cloud hosting cost?
A: Entry-level cloud hosting solutions are typically more expensive than cheap shared plans. However, they’re much more affordable than dedicated servers, and in the long run, they tend to be more cost-efficient because of the flexible hardware resource distribution.
Q: Is cloud hosting secure?
A: Yes, cloud hosting is inherently secure out of the box. This is because the environment doesn’t allow for a single point of breach. Instead of a single physical server, the system operates from a network of interconnected machines. This also makes it a harder target for DDoS attacks.
Compared to shared hosting, cloud technology is much safer. Due to virtualization, each user account is completely isolated from others, so your project is practically as secure as you can make it.
Q: What if my site outgrows cloud hosting?
A: One of the best advantages of this type of hosting is the lack of limitations on how much you can grow. In a traditional VPS setup, you can add as much resources as your physical server allows. But in a cloud configuration, you have multiple servers, which means your website can grow exponentially. Adding more CPU, RAM, or disk space is as simple as a button click, ensuring true scalability according to your needs.
What is a VPS – Everything you need to know!


